General News
Yiliang Shi receives honorable mention for the CRA's Outstanding Undergraduate Research Award

Congratulations to Yiliang Shi, who has been selected for honorable mention for the Computing Research Association's (CRA) Outstanding Undergraduate Research Award.
The award program recognizes undergraduate students in North American universities who show outstanding research potential in an area of computing research.
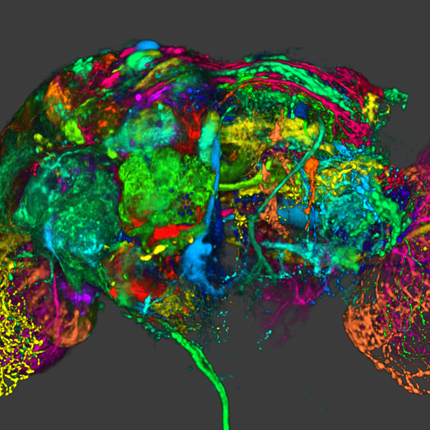
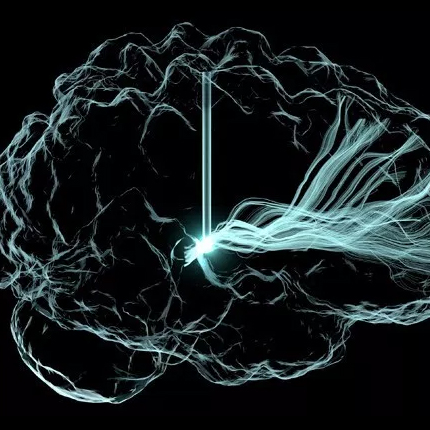
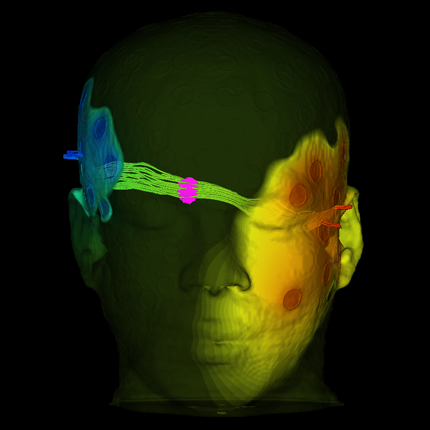
Technology from “Harry Potter” Movies Brings Magic of Brain into Focus
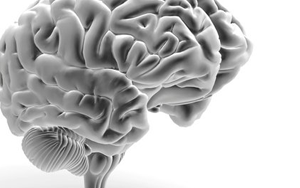 Software lets scientists explore the brain in 3-D and perform "virtual dissections"
Software lets scientists explore the brain in 3-D and perform "virtual dissections"
By Bahar Gholipour, Spectrum on November 19, 2017Article originally appears in Scientific American
The same techniques that generate images of smoke, clouds and fantastic beasts in movies can render neurons and brain structures in fine-grained detail.
Best Paper: CANDAR 17
Best Paper: ESPM2 2017
Air Quality & U, Empowering Citizens through Science
 Miriah Meyer and Kerry Kelly talk with KRCL's RadioActive, hosted by Billy Palmer and Lara Jones, on Air Quality and You: Empowering Citizens Through Science.
Miriah Meyer and Kerry Kelly talk with KRCL's RadioActive, hosted by Billy Palmer and Lara Jones, on Air Quality and You: Empowering Citizens Through Science. Low-cost commodity sensors are changing how cities and citizens measure and manage air quality. Through a suite of projects at the U we are building infrastructure that will enable real-time, fine-grained estimates of air quality both inside and outside of homes across Salt Lake City. In this presentation we’ll talk about the science of air quality, the computational challenges of developing rigorous air quality estimates, and our efforts to engage with citizens across the city.
Listen to the discussion on RadioActive
Valerio and Kree Receive IEEE Visualization 15 Year Test of Time Award
 Congratulations to Valerio Pascucci and Kree Cole-McLaughlin on receiving the IEEE Visualization 15 Year Test of Time Award for their paper "Efficient computation of the topology of level sets."
Congratulations to Valerio Pascucci and Kree Cole-McLaughlin on receiving the IEEE Visualization 15 Year Test of Time Award for their paper "Efficient computation of the topology of level sets."Using topological approaches to analyze level sets from scalar field has been an important branch of methods in the SciVis community. While the theories of contour trees had been known prior to this paper, efficient and robust computation of contour trees and other topological features from a discrete data set has been a challenge. In this paper, the authors provided a detailed account of the implementation of contour tree computation. The improved efficiency and the enhanced feature namely the Betti number makes the topological approach more practical and accessible to the scientific community. Considering the citation counts, the importance of the work, and the potential impact to the application areas, the SciVis Test of Time award committee selected this paper as the 2002 SciVis Test of Time award winner.
2017 NERSC Award for Innovative Use of HPC
https://www.nersc.gov/news-publications/nersc-news/nersc-center-news/2017/nersc/
Driving Visualization at the SH/EAHP Workshop 2017
 ViSOAR is set to drive the visualization for the 2017 Workshop on Molecular Genetics of Hematopoietic Neoplasms, September 7-9, in Chicago, IL.
ViSOAR is set to drive the visualization for the 2017 Workshop on Molecular Genetics of Hematopoietic Neoplasms, September 7-9, in Chicago, IL.The Scientific Computing and Imaging (SCI) Institute and the Center for Extreme Data Management, Analysis, and Visualization (CEDMAV), in collaboration with ARUP Laboratories and the University of Utah, Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy, have developed ViSOAR--a multi platform visualization application for accessing and processing very large imaging data.
SCI Acquires Nvidia DGX-1
 The SCI Institute, in partner with the School of Computing, is excited to announce the acquisition of an Nvidia DGX-1 deep learning system. This will be a shared resource that will be made available freely to all campus researchers interested in deep learning, machine learning and related areas.
The SCI Institute, in partner with the School of Computing, is excited to announce the acquisition of an Nvidia DGX-1 deep learning system. This will be a shared resource that will be made available freely to all campus researchers interested in deep learning, machine learning and related areas.Big data and machine learning are major factors shaping research and innovation now and will continue to be so in the foreseeable future. Deep learning represents the state-of-the-art in machine learning and data analysis.
Miriah Meyer Interviewed at Women in Data Science 2017
 Miriah Meyer, Assistant Professor of Computer Science at University of Utah, sits down with host Lisa Martin at Women in Data Science 2017, at Stanford University in Palo Alto, California.
Miriah Meyer, Assistant Professor of Computer Science at University of Utah, sits down with host Lisa Martin at Women in Data Science 2017, at Stanford University in Palo Alto, California.