SCI Publications
2012
K. Potter, P. Rosen, C.R. Johnson.
“From Quantification to Visualization: A Taxonomy of Uncertainty Visualization Approaches,” In Uncertainty Quantification in Scientific Computing, IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology Series, Vol. 377, Edited by Andrew Dienstfrey and Ronald Boisvert, Springer, pp. 226--249. 2012.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-32677-6_15
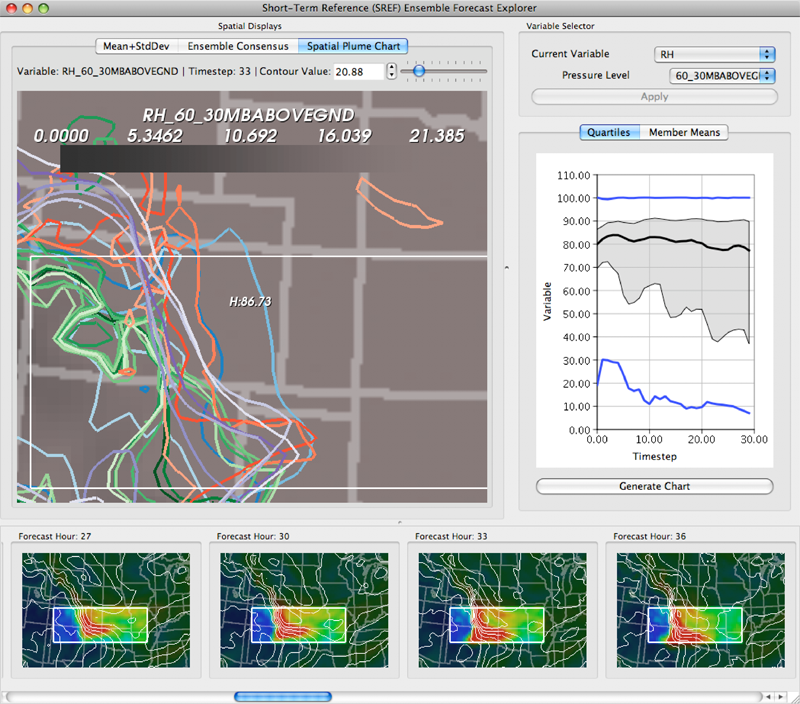
Keywords: scidac, netl, uncertainty visualization
P. Rosen, V. Popescu.
“Simplification of Node Position Data for Interactive Visualization of Dynamic Datasets,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (IEEE Visweek 2012 TVCG Track), pp. 1537--1548. 2012.
PubMed ID: 22025753
PubMed Central ID: PMC3411892
P. Rosen.
“Rectilinear Texture Warping for Fast Adaptive Shadow Mapping,” In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games (I3D '12), pp. 151--158. 2012.
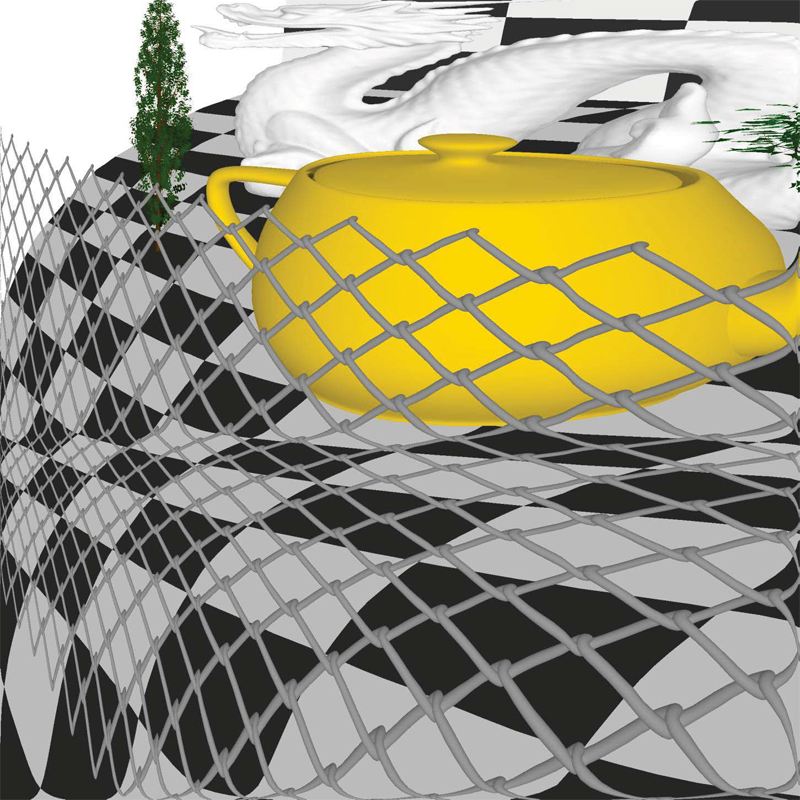
Conventional shadow mapping relies on uniform sampling for producing hard shadow in an efficient manner. This approach trades image quality in favor of efficiency. A number of approaches improve upon shadow mapping by combining multiple shadow maps or using complex data structures to produce shadow maps with multiple resolutions. By sacrificing some performance, these adaptive methods produce shadows that closely match ground truth.
This paper introduces Rectilinear Texture Warping (RTW) for efficiently generating adaptive shadow maps. RTW images combine the advantages of conventional shadow mapping - a single shadow map, quick construction, and constant time pixel shadow tests, with the primary advantage of adaptive techniques - shadow map resolutions which more closely match those requested by output images. RTW images consist of a conventional texture paired with two 1-D warping maps that form a rectilinear grid defining the variation in sampling rate. The quality of shadows produced with RTW shadow maps of standard resolutions, i.e. 2,048×2,048 texture for 1080p output images, approaches that of raytraced results while low overhead permits rendering at hundreds of frames per second.
Keywords: Rendering, Shadow Algorithms, Adaptive Sampling
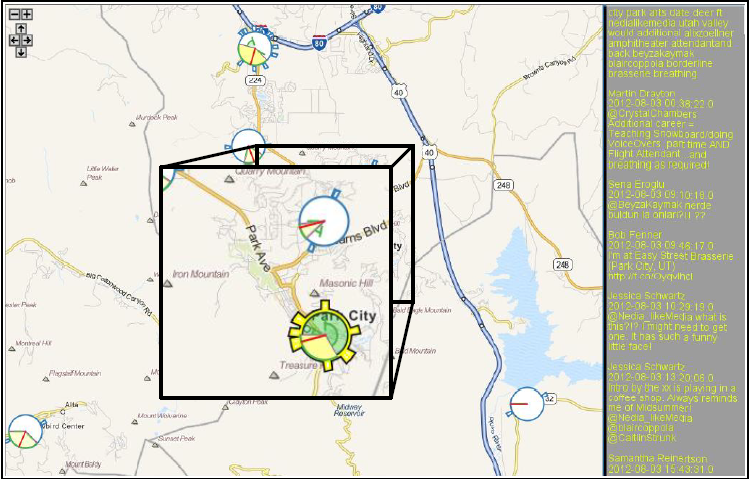
C. Yang, I. Jensen, P. Rosen.
“A Multiscale Approach to Network Event Identification using Geolocated Twitter Data,” In First IMC Workshop on Internet Visualization (WIV 2012), pp. (accepted). 2012.
2011
N. Andrysco, P. Rosen, V. Popescu, B. Benes, K.R. Gurney.
“Experiences in Disseminating Educational Visualizations,” In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (7th International Symposium on Visual Computing), Vol. 2, pp. 239--248. September, 2011.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-24031-7_24
A.N.M. Imroz Choudhury, P. Rosen.
“Abstract Visualization of Runtime Memory Behavior,” In 6th IEEE International Workshop on Visualizing Software for Understanding and Analysis (VISSOFT 2011), pp. 22--29. 2011.

P. Rosen, V. Popescu, K. Hayward, C. Wyman.
“Non-Pinhole Approximations for Interactive Rendering,” In IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, Vol. 99, 2011.
P. Rosen, V. Popescu.
“An Evaluation of 3-D Scene Exploration Using a Multiperspective Image Framework,” In The Visual Computer, Vol. 27, No. 6-8, Springer-Verlag New York, Inc., pp. 623--632. 2011.
DOI: 10.1007/s00371-011-0599-2
PubMed ID: 22661796
PubMed Central ID: PMC3364594
Multiperspective images (MPIs) show more than what is visible from a single viewpoint and are a promising approach for alleviating the problem of occlusions. We present a comprehensive user study that investigates the effectiveness of MPIs for 3-D scene exploration. A total of 47 subjects performed searching, counting, and spatial orientation tasks using both conventional and multiperspective images. We use a flexible MPI framework that allows trading off disocclusion power for image simplicity. The framework also allows rendering MPI images at interactive rates, which enables investigating interactive navigation and dynamic 3-D scenes. The results of our experiments show that MPIs can greatly outperform conventional images. For searching, subjects performed on average 28% faster using an MPI. For counting, accuracy was on average 91% using MPIs as compared to 42% for conventional images.
Keywords: Interactive 3-D scene exploration, Navigation, Occlusions, User study, Visual interfaces
2010
J. Cui, P. Rosen, V. Popescu, C. Hoffmann.
“A Curved Ray Camera for Handling Occlusions through Continuous Multiperspective Visualization,” In IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (Visualization 2010), pp. 1235--1242. November/December, 2010.
Page 2 of 2
