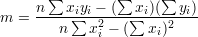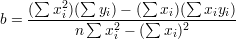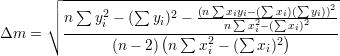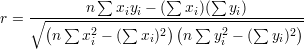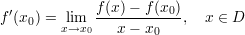
Definition:
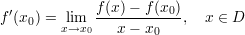
where 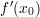 is the slope of the line tangent to
is the slope of the line tangent to 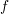 at
at 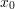 .
.
A function is said to have derivable at a point 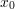 if it has finite derivate at that point, which happens
if the side derivates are equal. In that case
if it has finite derivate at that point, which happens
if the side derivates are equal. In that case
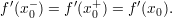
Properties of the derivatives:
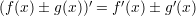
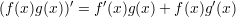
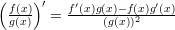
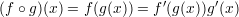
Derivates of some trigonometric functions:
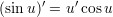
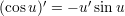
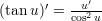
The fundamental equation of trigonometrics:
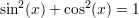
Sine and cosine as linear combinations of complex exponentials:
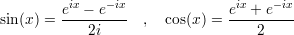
Useful formulas:
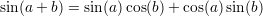
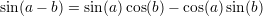
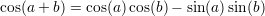
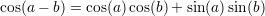
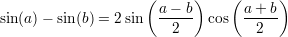

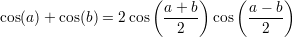
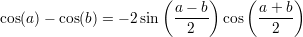
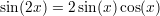
A function 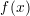 is said to be continous at some point
is said to be continous at some point  iff :
iff :
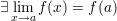
Some properties:
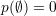
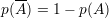
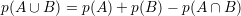
If two events are incompatibles or dijoint:
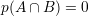
If two events are independent:
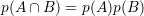
Conditional probability:
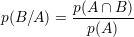
Binomial probability law:
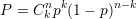
Factorial:
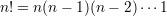
Ordered combinations without repetitions:
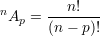
Ordered combinations with repetitions:
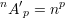
Unordered combinations without repetitions:
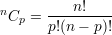
Some properties of unordered combinations without repetitions:
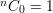
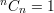
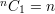
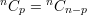
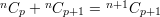
General formula:
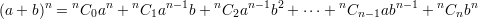
Some useful formulas from the particular case, 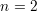 :
:
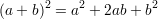
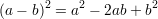
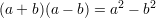
Definition:
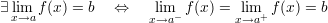
Some trigonometric limits:
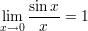
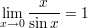
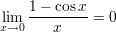
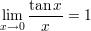
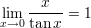
The Neper number related limits:
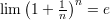
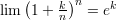
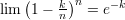
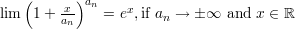
and the following theorems
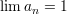 and
and 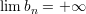 then,
then, 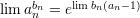 .
.
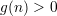 for all
for all 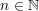 then,
then, 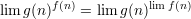 .
.
Definition:
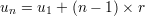
Sum of  elements of the progression:
elements of the progression:
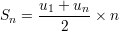
Definition:
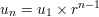
Sum of  elements of the progression:
elements of the progression:
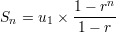
Sum of all the elements:
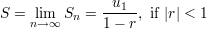
Variance of some data around the mean:
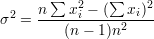
Principle of the error propagation:
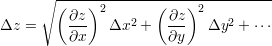
Linear regression ( ):
):