News
NVIDIA Center of Excellence Renewed
 The NVIDIA Corporation, the worldwide leader in visual computing technologies has renewed the University of Utah's recognition as a CUDA Center of Excellence, a milestone that marks the continuing of a significant partnership, starting in 2008, between the two organizations.
The NVIDIA Corporation, the worldwide leader in visual computing technologies has renewed the University of Utah's recognition as a CUDA Center of Excellence, a milestone that marks the continuing of a significant partnership, starting in 2008, between the two organizations.NVIDIA® CUDA™ technology is an award-winning C-compiler and software development kit (SDK) for developing computing applications on GPUs. Its inclusion in the University of Utah's curriculum is a clear indicator of the ground-swell that parallel computing using a many-core architecture is having on the high-performance computing industry. One of twenty-two centers, the University of Utah was the second school to be recognized as a CUDA Center of Excellence along with the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. Over 50 other schools and universities now include CUDA technology as part of their Computer Science curriculum or in their research.
U of U team finishes study of massive, mysterious explosion
 (KUTV) A team of researchers from the University of Utah is wrapping up an exhaustive five-year study looking into a mysterious explosion of a semi-truck in Spanish Fork Canyon back in 2005.
(KUTV) A team of researchers from the University of Utah is wrapping up an exhaustive five-year study looking into a mysterious explosion of a semi-truck in Spanish Fork Canyon back in 2005.The truck was packed with 35,000 pounds of mining explosives. It blew up after the truck rolled over, leaving a massive crater, 70-feet wide and 30-feet deep.
There were no fatalities but explosions like the one that happened on Aug. 10, 2005 are extremely rare. But the team of researchers is determined to prevent this type of incident from happening again.
Martin Berzins appointed Member of ASCAC
 Martin Berzins has been appointed a member of the Advanced Scientific Computing Advisory Committee (ASCAC). The committee provides advice and recommendations on scientific, technical, and programmatic issues relating to the ASCAC Program.
Martin Berzins has been appointed a member of the Advanced Scientific Computing Advisory Committee (ASCAC). The committee provides advice and recommendations on scientific, technical, and programmatic issues relating to the ASCAC Program.The Advanced Scientific Computing Advisory Committee (ASCAC), established on August 12, 1999, provides valuable, independent advice to the Department of Energy on a variety of complex scientific and technical issues related to its Advanced Scientific Computing Research program.
Learn more about ASCAC
Now Available: Spatio-temporal Image Analysis for Longitudinal and Time-Series Image Data
 S. Durrleman, P.T. Fletcher, G. Gerig, M. Niethammer, X. Pennec (Eds.)
S. Durrleman, P.T. Fletcher, G. Gerig, M. Niethammer, X. Pennec (Eds.)Third International Workshop, STIA 2014, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2014, Boston, MA, USA, September 18, 2014, Revised Selected Papers
Series: Image Processing, Computer Vision, Pattern Recognition, and Graphics, Vol. 8682, Springer LNCS
Simulations Aimed at Safer Transport of Explosives
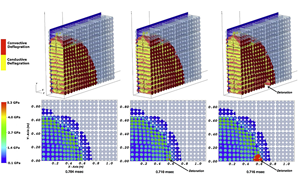 Credit: Jim Collins - Argonne Leadership Computing Facility
Credit: Jim Collins - Argonne Leadership Computing FacilitySee original article: "Simulations Aimed at Safer Transport of Explosives"
In 2005, a semi-truck hauling 35,000 pounds of explosives through the Spanish Fork Canyon in Utah crashed and caught fire, causing a dramatic explosion that left a 30-by-70-foot crater in the highway.
Fortunately, there were no fatalities. With about three minutes between the crash and the explosion, the driver and other motorists had time to flee. Some injuries did occur, however, as the explosion sent debris flying in all directions and produced a shock wave that blew out nearby car windows.
Now Available: Topological and Statistical Methods for Complex Data
 Edited by J. Bennett, F. Vivodtzev, V. Pascucci
Edited by J. Bennett, F. Vivodtzev, V. Pascucci- Latest peer-reviewed results in a growing research area
- Many applications in science and engineering
- Important contributions to the fields of mathematics and computer science
This book contains papers presented at the Workshop on the Analysis of Large-scale, High-Dimensional, and Multi-Variate Data Using Topology and Statistics, held in Le Barp, France, June 2013. It features the work of some of the most prominent and recognized leaders in the field who examine challenges as well as detail solutions to the analysis of extreme scale data.
Strong Showing for SCI Alumni at Vis 2014
 Congratulations to our former SCI Institute and SoC Colleague Claudio Silva, now at New York University Polytechnic School of Engineering, who was awarded the 2014 IEEE Visualization Technical Achievement Award at Vis 2014 in Paris. The award is in recognition of seminal advances in geometric computing for visualization and for contributions to the development of the VisTrails data exploration system.
Congratulations to our former SCI Institute and SoC Colleague Claudio Silva, now at New York University Polytechnic School of Engineering, who was awarded the 2014 IEEE Visualization Technical Achievement Award at Vis 2014 in Paris. The award is in recognition of seminal advances in geometric computing for visualization and for contributions to the development of the VisTrails data exploration system.See: Phys.Org "NYU professor wins premier award in the data visualization field."
School of Computing Recognized Among 50 Most Innovative CS Departments in the U.S.
 The University of Utah's School of Computing was recently recognized in Computer Science Degree HUB's list of The 50 Most Innovative Computer Science Departments in the U.S. The SCI Institute was also mentioned as a place where "students work side by side with distinguished scientists to come up with pioneering biomedical solutions."
The University of Utah's School of Computing was recently recognized in Computer Science Degree HUB's list of The 50 Most Innovative Computer Science Departments in the U.S. The SCI Institute was also mentioned as a place where "students work side by side with distinguished scientists to come up with pioneering biomedical solutions."
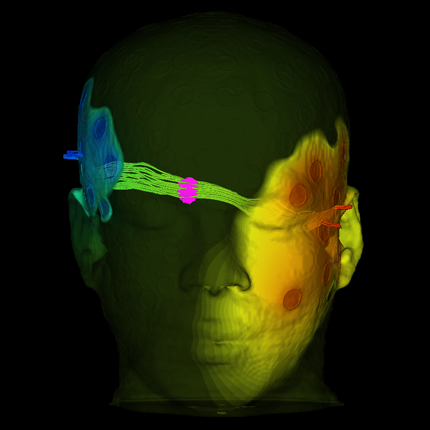
Treating Tremors
Dr. Christopher Butson Interviewed for AMS
 It may not sound like much fun having an electrode implanted in your brain, yet it's much better than not being able to hold anything even for a second, which can happen to someone with Parkinson's disease or essential tremor. Deep brain stimulation is effective in treating these conditions, but determining the proper stimulating parameters can take many hours and can require multiple visits by patients. Mathematics is part of a new approach that reduces the time needed to find optimal settings of the electrodes from several hours to a few minutes. First, mathematical models describe a person's brain accurately. Then systems of differential equations that represent neuron behavior are solved numerically. This combination allows doctors to see the results of different strategies in real time and speed their patients' return to normal lives.
It may not sound like much fun having an electrode implanted in your brain, yet it's much better than not being able to hold anything even for a second, which can happen to someone with Parkinson's disease or essential tremor. Deep brain stimulation is effective in treating these conditions, but determining the proper stimulating parameters can take many hours and can require multiple visits by patients. Mathematics is part of a new approach that reduces the time needed to find optimal settings of the electrodes from several hours to a few minutes. First, mathematical models describe a person's brain accurately. Then systems of differential equations that represent neuron behavior are solved numerically. This combination allows doctors to see the results of different strategies in real time and speed their patients' return to normal lives.
Now Available: Scientific Visualization
 Edited by Hansen, C.D., Chen, M., Johnson, C.R., Kaufman, A.E., Hagen, H.
Edited by Hansen, C.D., Chen, M., Johnson, C.R., Kaufman, A.E., Hagen, H.Based on a seminar that took place in Dagstuhl, Germany, this contributed volume studies four important topics within scientific visualization: uncertainty visualization, multifield visualization, biomedical visualization and scalable visualization.
- Uncertainty visualization deals with uncertain data from simulations or sampled data, uncertainty due to the mathematical processes operating on the data, and uncertainty in the visual representation,
- Multifield visualization addresses the need to depict multiple data at individual locations and the combination of multiple datasets,
- Biomedical is a vast field with select subtopics addressed from scanning methodologies to structural applications to biological applications,
- Scalability in scientific visualization is critical as data grows and computational devices range from hand-held mobile devices to exascale computational platforms.
Best Paper Award at MICCAI 2014
 Congratulations to PhD student Miaomiao Zhang, who won the MICCAI 2014 Young Scientist Award (a.k.a., best paper award) for her paper:
Congratulations to PhD student Miaomiao Zhang, who won the MICCAI 2014 Young Scientist Award (a.k.a., best paper award) for her paper:M. Zhang, P. T. Fletcher, Bayesian Principal Geodesic Analysis in Diffeomorphic Image Registration, MICCAI 2014.
MICCAI is the premiere venue in medical image analysis with ~1000 attendees.